随说 : 本文结合自己做的这个项目来整理开发思路,这一篇着重 <蓝牙> 交互模块
前期准备 :
- 硬件商家提供的电路板
- 硬件商家提供的电路板通讯协议
看懂通讯协议
我模拟了一份通讯协议的资料,凑合着看吧
当然,实际情况的指令会多的多
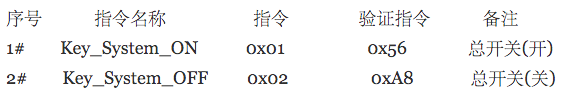
序号 : 指令的序号(没啥意义)
指令名称 : 就是给指令定义一个名字,一般可以作为储存 本地的Key
指令 : 实际操作电脑版接收的数据
验证指令 : 根据一个验证算法得出的数据.
备注 : 告诉你这个是干嘛的.
连接设备
将电路板通电,然后它就处于可被检测状态.
作为App来说,首先需要检测iphone是否处于蓝牙开启状态
1、创建Central管理器
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| // 创建Central管理器,这里我弄成单例
+(LinBlueToothEngine *)shareInstance
{
static dispatch_once_t pred = 0;
__strong static LinBlueToothEngine *_sharedObject = nil;
dispatch_once(&pred, ^{
_sharedObject = [[LinBlueToothEngine alloc] init];
});
return _sharedObject;
}
|
2、检测蓝牙状态
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| // 当创建Central管理器成功后,系统会自动调用该方法
// 该方法的作用是检测蓝牙开启状态
- (void)centralManagerDidUpdateState:(CBCentralManager *)central
{
// 具体又几种状态的,这里忽略
switch ([central state])
{
case CBCentralManagerStatePoweredOn:
_state = @"正常打开了";
_bluetoothPowerOn = YES;
// 注意这句, 调用CoreBluetooth框架 CBCentralManager类的
//scanForPeripheralsWithServices: options: 方法
[self.centralManager scanForPeripheralsWithServices:nil options:nil];
break;
case CBCentralManagerStateUnknown:
default:
;
}
NSLog(@"蓝牙此时状态: %@", _state);
}
|
确保蓝牙打开,才能扫描设备
3、扫描设备
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| //搜索成功的回调
- (void)centralManager:(CBCentralManager *)central didDiscoverPeripheral:(CBPeripheral *)peripheral advertisementData:(NSDictionary *)advertisementData RSSI:(NSNumber *)RSSI{ //BLUETOOTH_DEVICE_NAME 为设备名的宏定义
if ([peripheral.name isEqualToString:BLUETOOTH_DEVICE_NAME]) {
// 保存peripheral
self.deviceModel.peripheral = peripheral;
//执行搜索成功的block
!self.scanningToAroundYES ? : self.scanningToAroundYES(peripheral.name);
}
}
|
4、连接蓝牙设备
1
2
3
4
| //连接蓝牙设备
-(void)startconnectService{
[self.centralManager connectPeripheral:self.deviceModel.peripheral options:@{CBConnectPeripheralOptionNotifyOnConnectionKey :@YES}];
}
|
5、连接成功
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| //外设连接成功
- (void)centralManager:(CBCentralManager *)central didConnectPeripheral:(CBPeripheral *)peripheral{
if ([peripheral.name isEqualToString:BLUETOOTH_DEVICE_NAME]) {
if (peripheral == self.deviceModel.peripheral) {
self.deviceModel.peripheral.delegate = self;
[self.deviceModel.peripheral discoverServices:nil];
}
}
}
|
6、发现外设
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| //发现外设的service
- (void)peripheral:(CBPeripheral *)peripheral didDiscoverServices:(NSError *)error{
if (error){
!self.connentionFailure ? :self.connentionFailure();
return;
}
if ([peripheral.name isEqualToString:BLUETOOTH_DEVICE_NAME]){
for (CBService *service in peripheral.services){
if ([service.UUID isEqual:[CBUUID UUIDWithString:BLUETOOTH_CBUUID]]){
[peripheral discoverCharacteristics:nil forService:service];
}
}
}
}
|
7、发现service的特征
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| // 外设发现service的特征
- (void)peripheral:(CBPeripheral *)peripheral didDiscoverCharacteristicsForService:(CBService *)service error:(NSError *)error{
if (error) {
return;
}
if ([peripheral.name isEqualToString:BLUETOOTH_DEVICE_NAME]){
if (peripheral == self.deviceModel.peripheral) {
for (CBCharacteristic *characteristic in service.characteristics) {
if ([characteristic.UUID isEqual:[CBUUID UUIDWithString:WRITE_CHARACTERISTIC]]) {
NSLog(@"写入特征");
self.deviceModel.characteristcs = characteristic;
}else if ([characteristic.UUID isEqual:[CBUUID UUIDWithString:READ_CHARACTERISTIC]]){
NSLog(@"通知特征");
[self.deviceModel.peripheral setNotifyValue:YES forCharacteristic:characteristic];
}
}
}
!self.connectionSuccess ? : self.connectionSuccess ();
}
}
|
8、传输数据
characteristic 有几种属性
Read : 只读
Write Without Response : 写数据不接收回执
Write : 只写
Notify : 通知(不需要对方回复)
Indicate : 通知(需要回复)
这个项目中,只用到了write 与 notify
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| //发送指令
- (IBAction)sendCommand:(id)sender {
NSString *command = @"02******";
//将16进制的字符串转16位Data
NSData *data = [command stringHexToBytesData];
[self.blueToothEngine sendWriteData:data];
}
- (void)sendWriteData:(NSData *)data{
[self.deviceModel.peripheral writeValue:data forCharacteristic:self.deviceModel.characteristcs type:CBCharacteristicWriteWithResponse];
}
//接收电路板回来的信息
- (void)peripheral:(CBPeripheral *)peripheral didUpdateValueForCharacteristic:(CBCharacteristic *)characteristic error:(NSError *)error{
if (error) {
return;
}
if ([peripheral.name isEqualToString:BLUETOOTH_DEVICE_NAME]) {
if (peripheral == self.deviceModel.peripheral) {
//解析数据
NSString *resultString = [[NSString stringWithHexData:characteristic.value] stringUpperCase];
//将数据返回页面
!self.dataReportingBluetooth ? : self.dataReportingBluetooth(resultString);
}
}
}
|
蓝牙硬件版本升级
最近给产品做了DFU升级
其实DFU升级是app端和驱动这边共同完成的,这个协议是自己定义的,所以每个公司的升级都不一样,但从根本上看都是一样的,就是把升级包发给固件,然后进行升级,下面就来简单的说下我们这边的步骤。
1、发送升级指令
就是给固件发送一个指令,告诉固件,进入升级模式,当然在这之前有的公司会先发送一个查询固件的版本,然后对比当前版本和最新版,看是否需要升级,如果需要,再发送升级指令。这时,固件一般会断开蓝牙,切换成升级模式。
2、发送升级包
当固件切换完模式以后,需要重新连接蓝牙;这一步就是将升级包发送给固件了,由于蓝牙每次发送数据大小的限制,升级包一般都要分多次发送,每次发送一部分。
3、校验重启
当整个升级包都发送给固件以后,固件就会进行升级,升级完成之后固件就可以重启,把模式切换回正常使用模式了。对此,整个升级就完成了,还是前面说的,升级是和驱动这边共同完成的,双方定义如何升级,但总的都是获取升级包,发送给固件,固件进行升级这样。
注意:有的公司会把升级包放到服务器,也有的公司会在更新App时将固件升级包放到App里,毕竟固件升级的频率还是很低的,能不升级则尽量不要升级。
项目示例地址
