AFNetworking是iOS开发中一个常用的网络请求第三方框架,我们常会这样子去发起一个请求
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 NSString *url = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"https://test?type=%@" ,@"test" ]; AFHTTPSessionManager *manager = [AFHTTPSessionManager manager]; [manager GET:url parameters:nil progress:^(NSProgress * _Nonnull downloadProgress) { } success:^(NSURLSessionDataTask * _Nonnull task, id _Nullable responseObject) { NSLog (@"success = %@" ,responseObject); } failure:^(NSURLSessionDataTask * _Nullable task, NSError * _Nonnull error) { NSLog (@"failure = %@" ,error); }];
先来看看它在GitHub 上是怎么解释的:
AFNetworking is a delightful networking library for iOS, macOS, watchOS, and tvOS. It’s built on top of the Foundation URL Loading System, extending the powerful high-level networking abstractions built into Cocoa. It has a modular architecture with well-designed, feature-rich APIs that are a joy to use.
大体来讲,就是上面字面上的意思啦,总结来讲就三个:网络库,高级网络抽象,丰富的api。
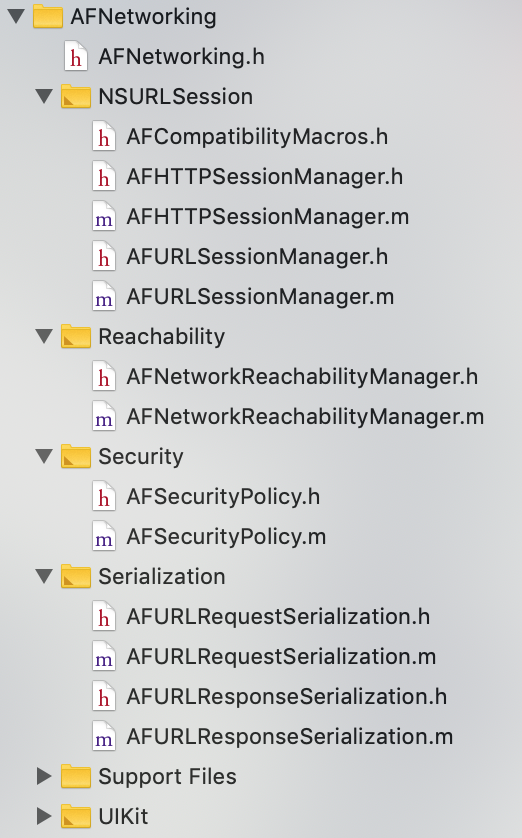
框架组成
我们一起来看看AFNetworking的框架组成:
从上面看,分为五大块
第一大块
AFURLSessionManager为AFNetworking的核心类,AFNetworking所展开的工作都会围绕这个类来进行,同样,AFNetworking有一个子类继承了它,这个类是AFHTTPSessionManager,它主要负责我们当前的业务逻辑处理
第二大块
请求的时候,我们需要做序列化,Serialization文件夹里就包含了我们请求和相应的序列化,这个序列化对于我们请求来说,它可能主要用来参数的拼接,header,parameters,多表单参数的提交,而对于当前的response,它取决于我们怎么去序列化返回来的数据是以二进制、json、xml,它都有不同的类去实现具体的功能,总的来说,Serialization这个文件夹里的类是处理序列化的,这个序列化分为请求和响应的序列化
第三大块
AFNetworlingReachabilityManager这个类相信大家对于这个应该不陌生,我们常常在开发中会有网络状态监测的需求,这个是类就是用来做网络检测的
第四大块
Security文件夹里的类,它是用来做安全认证的,比如证书的一些校验逻辑就是在这里面
第五大块
UIKit那个文件夹它是一个简单的扩展,它用来便利的提供我们的UI层来调用我们的业务逻辑
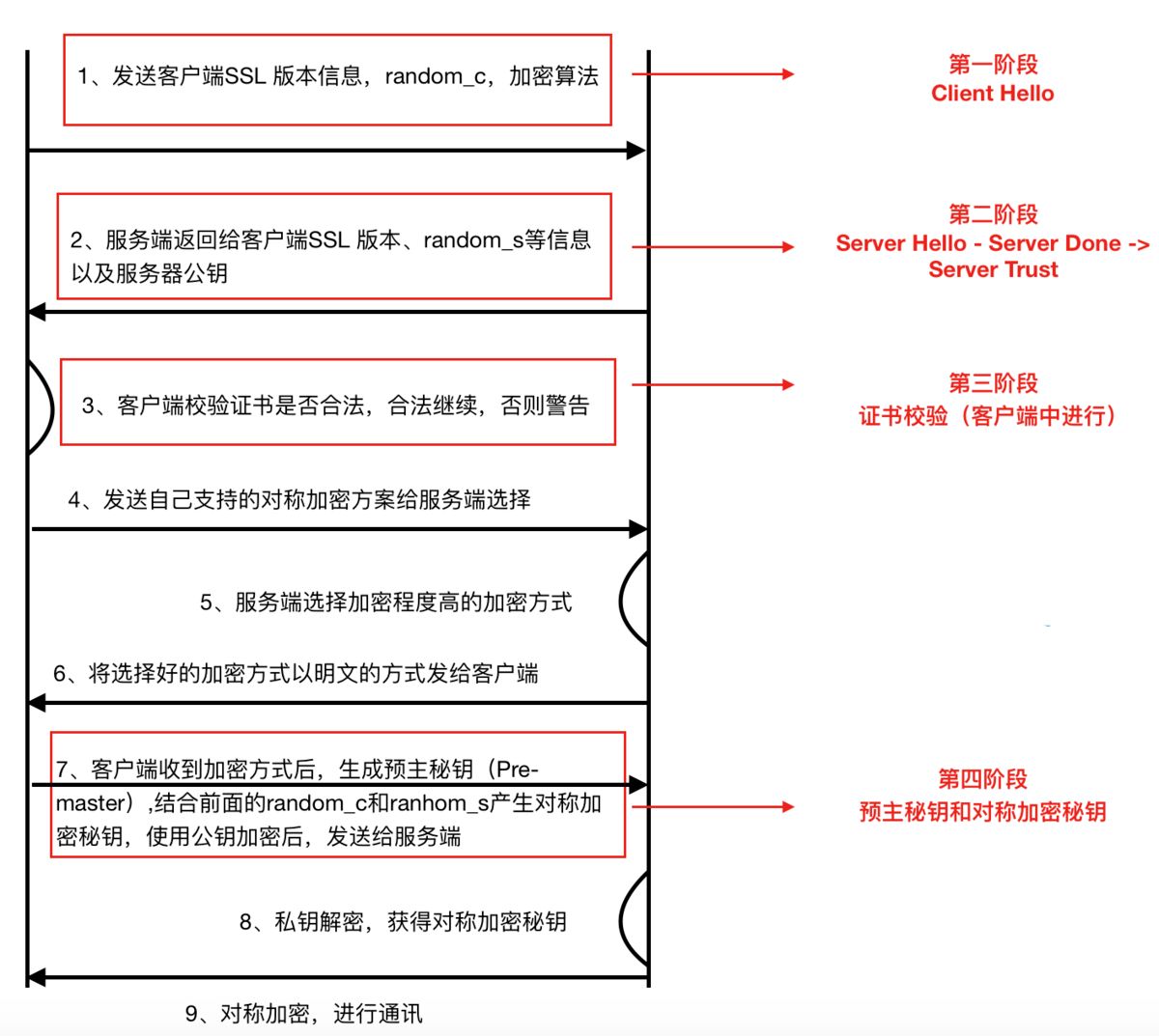
在探究更深入的层面之前,我们先说说HTTPS的流程,方便后面讲解的扩展
版本信息:包含了随机数(random_c/random_s),支持的加密算法等信息,通过TCP发送给服务端;
证书校验
AFURLSessionManager是AFNetworking的核心类,它所展开的工作都是围绕这个来进行的,那我们就从这个类开始看起,看看是不是真的如所说的,它是一个管理控制中心类。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 - (void )URLSession:(NSURLSession *)session didReceiveChallenge:(NSURLAuthenticationChallenge *)challenge completionHandler:(void (^)(NSURLSessionAuthChallengeDisposition disposition, NSURLCredential *credential))completionHandler { NSURLSessionAuthChallengeDisposition disposition = NSURLSessionAuthChallengePerformDefaultHandling ; __block NSURLCredential *credential = nil ; if (self .sessionDidReceiveAuthenticationChallenge) { disposition = self .sessionDidReceiveAuthenticationChallenge(session, challenge, &credential); } else { if ([challenge.protectionSpace.authenticationMethod isEqualToString:NSURLAuthenticationMethodServerTrust ]) { if ([self .securityPolicy evaluateServerTrust:challenge.protectionSpace.serverTrust forDomain:challenge.protectionSpace.host]) { credential = [NSURLCredential credentialForTrust:challenge.protectionSpace.serverTrust]; if (credential) { disposition = NSURLSessionAuthChallengeUseCredential ; } else { disposition = NSURLSessionAuthChallengePerformDefaultHandling ; } } else { disposition = NSURLSessionAuthChallengeCancelAuthenticationChallenge ; } } else { disposition = NSURLSessionAuthChallengePerformDefaultHandling ; } } if (completionHandler) { completionHandler(disposition, credential); } } 这里有几个点要说一下,
tip1[challenge.protectionSpace.authenticationMethod isEqualToString:NSURLAuthenticationMethodServerTrust]
1 2 3 4 5 @property (readonly , copy ) NSURLProtectionSpace *protectionSpace;
AFNetworking自己也说了,这是一个需要认证的保护空间,那我们再点进去看下,这回我们就能看到了
1 2 3 4 5 @property (readonly , copy ) NSString *authenticationMethod;
以上,就有了接收服务器挑战的方法的判断
tip2[self.securityPolicy evaluateServerTrust:challenge.protectionSpace.serverTrust forDomain:challenge.protectionSpace.host]
1 @property (nonatomic , strong ) AFSecurityPolicy *securityPolicy;
Security是用来做安全认证的,那这里是不是来验证服务端是否值得信任的?(知识点慢慢串起来了哈)我们点进去看看:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 - (BOOL )evaluateServerTrust:(SecTrustRef)serverTrust forDomain:(NSString *)domain { if (domain && self .allowInvalidCertificates && self .validatesDomainName && (self .SSLPinningMode == AFSSLPinningModeNone || [self .pinnedCertificates count] == 0 )) { NSLog (@"In order to validate a domain name for self signed certificates, you MUST use pinning." ); return NO ; } NSMutableArray *policies = [NSMutableArray array]; if (self .validatesDomainName) { [policies addObject:(__bridge_transfer id )SecPolicyCreateSSL(true , (__bridge CFStringRef )domain)]; } else { [policies addObject:(__bridge_transfer id )SecPolicyCreateBasicX509()]; } SecTrustSetPolicies(serverTrust, (__bridge CFArrayRef )policies); if (self .SSLPinningMode == AFSSLPinningModeNone) { return self .allowInvalidCertificates || AFServerTrustIsValid(serverTrust); } else if (!AFServerTrustIsValid(serverTrust) && !self .allowInvalidCertificates) { return NO ; } switch (self .SSLPinningMode) { case AFSSLPinningModeNone: default : return NO ; case AFSSLPinningModeCertificate: { NSMutableArray *pinnedCertificates = [NSMutableArray array]; for (NSData *certificateData in self .pinnedCertificates) { [pinnedCertificates addObject:(__bridge_transfer id )SecCertificateCreateWithData(NULL , (__bridge CFDataRef )certificateData)]; } SecTrustSetAnchorCertificates(serverTrust, (__bridge CFArrayRef )pinnedCertificates); if (!AFServerTrustIsValid(serverTrust)) { return NO ; } NSArray *serverCertificates = AFCertificateTrustChainForServerTrust(serverTrust); for (NSData *trustChainCertificate in [serverCertificates reverseObjectEnumerator]) { if ([self .pinnedCertificates containsObject:trustChainCertificate]) { return YES ; } } return NO ; } case AFSSLPinningModePublicKey: { NSUInteger trustedPublicKeyCount = 0 ; NSArray *publicKeys = AFPublicKeyTrustChainForServerTrust(serverTrust); for (id trustChainPublicKey in publicKeys) { for (id pinnedPublicKey in self .pinnedPublicKeys) { if (AFSecKeyIsEqualToKey((__bridge SecKeyRef)trustChainPublicKey, (__bridge SecKeyRef)pinnedPublicKey)) { trustedPublicKeyCount += 1 ; } } } return trustedPublicKeyCount > 0 ; } } return NO ; }
(1)if (domain && self.allowInvalidCertificates && self.validatesDomainName && (self.SSLPinningMode == AFSSLPinningModeNone || [self.pinnedCertificates count] == 0)) {...}
(2) NSMutableArray *policies = [NSMutableArray array]; 装验证策略
1 2 3 4 5 if (self .validatesDomainName) { [policies addObject:(__bridge_transfer id )SecPolicyCreateSSL(true , (__bridge CFStringRef )domain)]; } else { [policies addObject:(__bridge_transfer id )SecPolicyCreateBasicX509()]; }
生成验证策略。如果要验证域名,就以域名为参数创建一个策略,否则创建默认的basicX509策略SecTrustSetPolicies(serverTrust, (__bridge CFArrayRef)policies);
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 if (self .SSLPinningMode == AFSSLPinningModeNone) { return self .allowInvalidCertificates || AFServerTrustIsValid(serverTrust); } else if (!AFServerTrustIsValid(serverTrust) && !self .allowInvalidCertificates) { return NO ; }
看上面注释case AFSSLPinningModeCertificate: {...}
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 case AFSSLPinningModeCertificate: { NSMutableArray *pinnedCertificates = [NSMutableArray array]; for (NSData *certificateData in self .pinnedCertificates) { [pinnedCertificates addObject:(__bridge_transfer id )SecCertificateCreateWithData(NULL , (__bridge CFDataRef )certificateData)]; } SecTrustSetAnchorCertificates(serverTrust, (__bridge CFArrayRef )pinnedCertificates); if (!AFServerTrustIsValid(serverTrust)) { return NO ; } for (NSData *trustChainCertificate in [serverCertificates reverseObjectEnumerator]) { if ([self .pinnedCertificates containsObject:trustChainCertificate]) { return YES ; } } return NO ; }
(7)case AFSSLPinningModePublicKey: {...}
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 case AFSSLPinningModePublicKey: { NSUInteger trustedPublicKeyCount = 0 ; NSArray *publicKeys = AFPublicKeyTrustChainForServerTrust(serverTrust); for (id trustChainPublicKey in publicKeys) { for (id pinnedPublicKey in self .pinnedPublicKeys) { if (AFSecKeyIsEqualToKey((__bridge SecKeyRef)trustChainPublicKey, (__bridge SecKeyRef)pinnedPublicKey)) { trustedPublicKeyCount += 1 ; } } } return trustedPublicKeyCount > 0 ;
以上就是这个方法 - (BOOL)evaluateServerTrust:(SecTrustRef)serverTrust forDomain:(NSString *)domain 里的所有逻辑啦
static BOOL AFServerTrustIsValid(SecTrustRef serverTrust) {...}__Require_noErr_Quiet(SecTrustEvaluate(serverTrust, &result), _out);
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 static BOOL AFServerTrustIsValid(SecTrustRef serverTrust) { BOOL isValid = NO ; SecTrustResultType result; __Require_noErr_Quiet(SecTrustEvaluate(serverTrust, &result), _out ); isValid = (result == kSecTrustResultUnspecified || result == kSecTrustResultProceed); _out : return isValid; }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 credential = [NSURLCredential credentialForTrust:challenge.protectionSpace.serverTrust]; if (credential) { disposition = NSURLSessionAuthChallengeUseCredential ; } else { disposition = NSURLSessionAuthChallengePerformDefaultHandling ; }
如果信任评估通过,就从受保护空间里面拿出证书,回调给服务器,告诉服务,我信任你,你给我发送数据吧。如果信任评估没有通过,则取消挑战。
总的来说,HTTPS证书效验的过程就是这样子的啦。
1、证书链:是根证书以及根证书颁发的子证书组成的一系列证书链